Introduction to CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
We will cover the following:
CSS Frontmatter
- The purpose of CSS is used to manipulate how your HTML webpage is visually presented or “styled”.
- The “Cascading” in CSS is that there is an inherent hierarchy of the styling rules upon an element. So, multiple style sources can apply to a single webpage (HTML) element.
- Validation of CSS: css-validator
- CSS is converted into the DOM (Document Object Model; representation of the computer’s memory) to be combined with HTML content. The browser displays the contents of the DOM. (We do not cover this in this lecture, but you can read more about this here, here, here, and here.)
- As a general introduction as to the purpose of CSS, let’s walk through a 4-minute guide on web design found here.
- CSS3 (latest version) has media queries which allow you to specify the context of the CSS style (print, screen with a certain width, etc.). We will not be covering these in this lecture.
CSS Code Location
-
Inline: We can add styles within a
styleattribute of HTML tags.<h1 style="color: red">Create My First Website</h1> - Internal/Header: We can add more general styles within a
styletag in the HTML document header.<head> <title>HTML Programming Example</title> <style> h1 { color: red; } </style> </head>Note: This applies to all tags unless specifying more detailed contexts (described later in the selectors section).
- External File: This is the preferred method for projects so that we can separate the CSS code from the HTML code.
<head> <title>HTML Programming Example</title> <link href="style.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"> </head>
Whether using the external file or the header approach, CSS is meant to be readible and thus white space is ignored, semicolons are used to end property lines, and squiggly brackets are used to encapsulate each selector or rule.
There is a way to write shorthand to combine properties one a single line, but we will not cover this within this lecture.
Hierarchy:
There is an order to the cascade of styles when applied to a single HTML element: importance, specificity, and source order. Here is a document that details this cascading effect in more detail.
Given the following CSS:
/* A */
p.class1[attr='value']
/* B */
p.class1 { }
/* C */
p.class2 { }
/* D */
p { }
/* E */
p { property: value !important; }
and the following HTML:
<p style='/*F*/ property:value;' class='class1 class2' attr='value'>
The cascade is as follows:
- E has the highest precedence because of the keyword
!important. It is recommended that you avoid its usage. - F is next, because it is an inline style.
- A is next, because it is more “specific” than anything else. It has 3 specifiers: The name of the element
p, its classclass1, an attributeattr='value'. - C is next, even though it has the same specificity as B. This is because it appears after B.
- B is next.
- D is the last one.
Comments
Comments in CSS only have one style:
/* Handle basic element styling */
body {
font-size: 62.5% /* 1em = 10px */
}
CSS Selectors
CSS selectors act similar to HTML elements:
div { ... }
<div>...</div>
<div>...</div>
However, the use of CSS can allow us to reduce the amount of HTML code we need:
p {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
}
<p><strong><i>Some text.</i></strong></p>
<p><strong><i>Some more text.</i></strong></p>
Types of CSS selectors:
- Universal (*)
* { padding: 5px; border: 1px solid black; background: rgba(255,0,0,0.25) } - Element (h1)
h1 { font-size: 20px; } p { color: green; } - Class (.classname)
.container { margin: 10px; }<div class='container'> <h1> This is heading </h1> </div> - ID (#idname) - can only be assigned to one element (link) but are like class selectors
#para1 { color: green; font-size: 16px; }<div> <p id='para1'> This is a paragraph </p> </div>
CSS selectors can also be combined to add specificity to certain elements:
.hotdog p {
background: brown;
}
.hotdog p.mustard {
background: yellow;
}
<div class="hotdog">
<p>...</p>
<p>...</p>
<p class="mustard">...</p>
</div>
Note: there are further selectors such as pseudo-classes, but that is more specific to context or the state of a HTML element such as :hover when a user hovers over that element.
Typography
Fonts
The main properties to style text on a web page are as follows:
- color (see below)
- font-family
- font-size
- font-weight
- line-height
There is also text decoration, alignment, indentation, shadows, transformations, spacing, and so much more.
Colors
Colors can be specified using keywords, hexadecimal values, RGB, RGBa, HSL, and HSLa values. Hexadecimal values are the most popular method.
html {
color: #555;
}
To see all of this typography at one glance:
<h2><a href="#">I Am a Builder</a></h2>
<p class="byline">Posted by Shay Howe</p>
<p>Every day I see designers and developers working alongside one another. They work intelligently in pursuit of business objectives. They work diligently making exceptional products. They solve real problems and take pride in their work. They are builders. <a href="#">Continue…</a></p>
h2,
p {
color: #555;
font: 13px/20px "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
}
a {
color: #0087cc;
}
a:hover {
color: #ff7b29;
}
h2 {
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 6px;
}
.byline {
color: #9799a7;
font-family: Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif;
font-style: italic;
margin-bottom: 18px;
}
The Box Model
Every HTML element can be thought of as a box and can be modified as such with relevant properties shown below:

Let’s see if we can find the total width and height of a sample element below (in pixels):
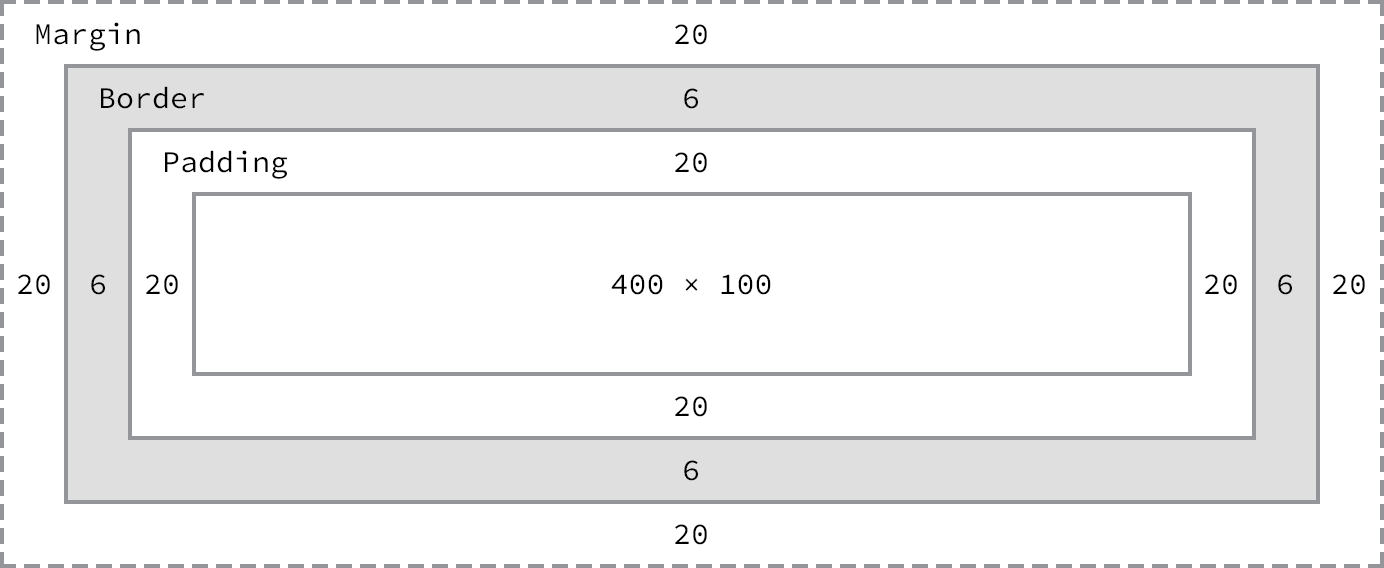
This allows one to position and manipulate each of the elements. In addition to this model, there are properties of the “box” such as:
- overflow (auto, hidden, visible)
- clipping (to trim the box’s overflow)
- outline
Types of boxes:
- block (stacked upon other boxes)
- inline (flows with document’s text)
- inline-block (combination of the prior two)
Resources
- cssreference.io: A good page reference of different types of css attributes
- css weekly: A css-centric email newsletter
- Code Academy
- BEM (Box Element Modifier)
- CSS Layout Tutorial
- Web Design in 4 minutes
- Code Guide by @mdo
- Web Technologies - Mozilla
- CSS Diner: Fun website that gives you practice on selectors
- CSS Selectors
- Can I Use: Helpful website on browser compatibility
- CSS Learning
- CSS Huge Learning Resource
- CSS on Solo Learn
- CSS Documentation Reference
- Bootstrap CSS: A good packaged CSS style made for you to use.
- CSS Zen Garden: A website that is fun to manipulate with very many examples from others.
- Learn to Code HTML & CSS: A great resource for both HTML and CSS
- Smashing Magazine Article
- Learn X in Y Minutes: CSS: A one-page document reference.
- My Device: Let’s you see the properties of your current browser window.
Online Editors
Below are online, interactive playgrounds that allow you to use HTML, CSS, and Javascript for coding and testing:
- My Recommendations:
- Others:
- Firefox Developer Tools: In-browser tools that Mozilla has developed.
- Dabblet: Only HTML and CSS
- JSBin
